The world of bullet trains is fascinating, blending high-speed travel with cutting-edge technology. These marvels of engineering have revolutionized the way we think about distance and time, and they continue to evolve. From their origins to their impact on the environment, bullet trains are a testament to human ingenuity and the quest for efficiency.
The Origin of Bullet Trains
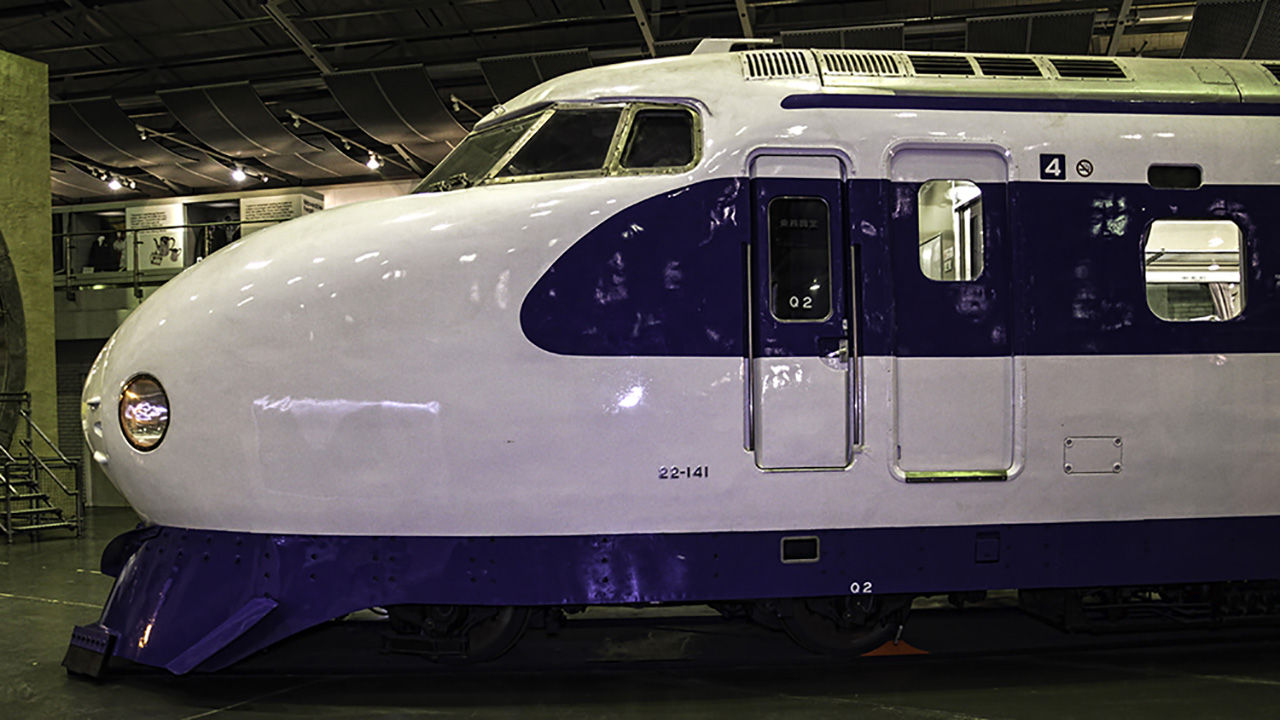

The concept of high-speed rail travel was first realized in Japan with the introduction of the Shinkansen in 1964. The first line connected Tokyo and Osaka, drastically reducing travel time between these two major cities. This innovation was motivated by the need to accommodate increased travel demands during Japan’s post-war economic boom. The Shinkansen, translating to “new trunk line,” was the beginning of a global high-speed rail revolution that set the standard for future developments in the field.
These trains were dubbed “bullet trains” due to their aerodynamic shape and rapid speed. The original Shinkansen could reach speeds of up to 210 km/h (130 mph), which was unprecedented at the time. This pioneering initiative demonstrated the potential of high-speed rail to both Japan and the world, influencing subsequent projects in other countries.
Speed Records of Bullet Trains
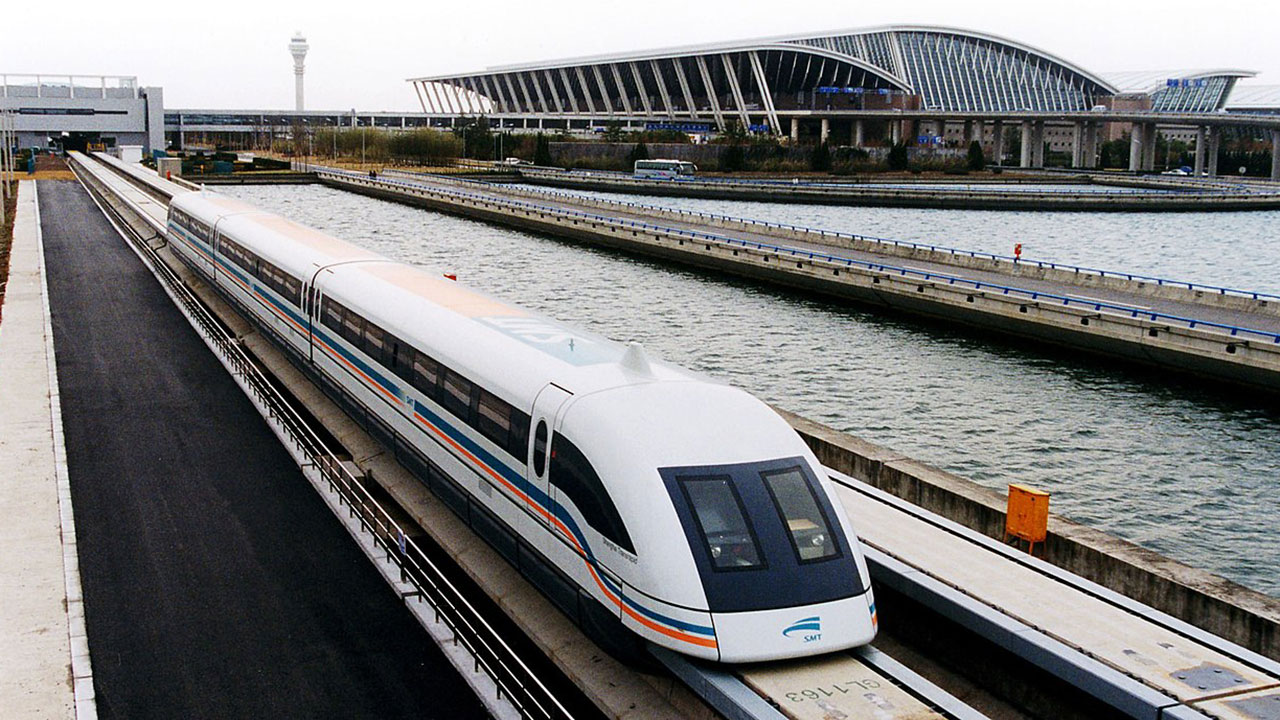

Bullet trains are known for their impressive speed. The current speed record for a commercial train is held by Japan’s L0 Series Maglev, which achieved a staggering 603 km/h (375 mph) during a test run in 2015. This magnetic levitation train uses powerful magnets to lift and propel the train, reducing friction and allowing for higher speeds. While not yet in commercial operation, it represents the future potential of rail travel.
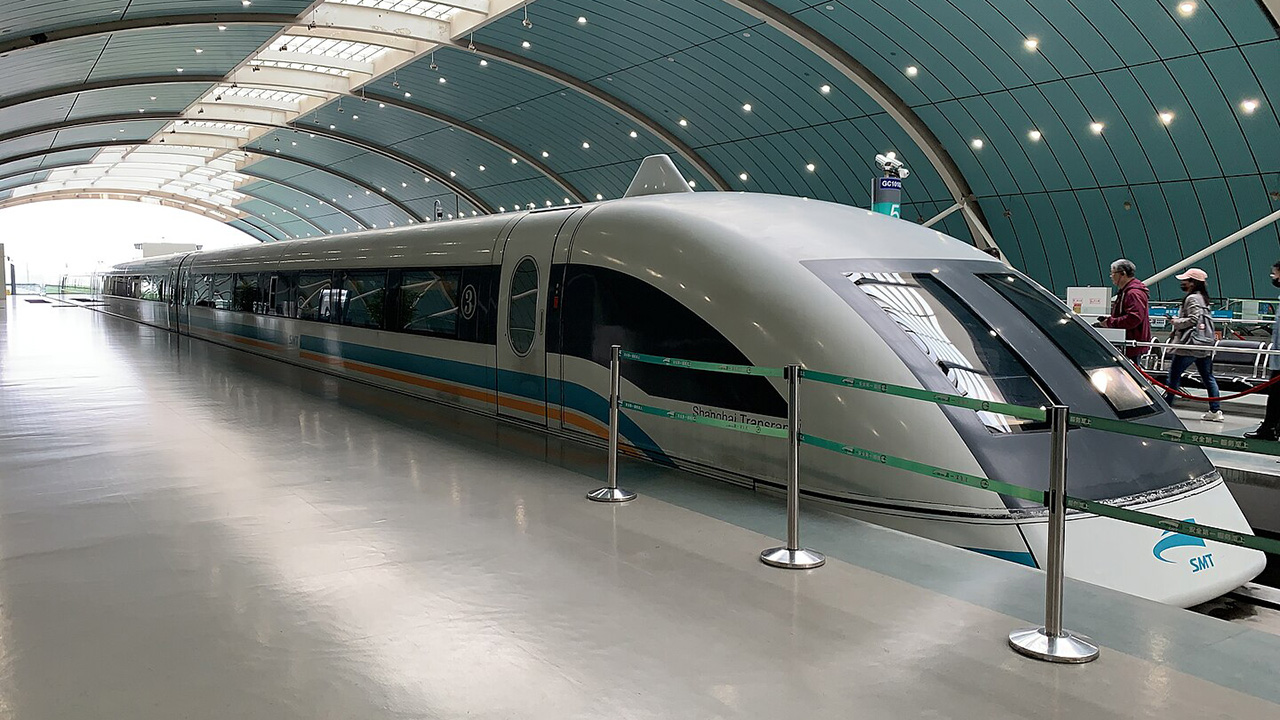
In regular service, the fastest operating bullet train is the Shanghai Maglev in China, which reaches speeds of 431 km/h (268 mph). Other notable mentions include France’s TGV, which has achieved speeds of 574.8 km/h (357.2 mph) during tests, though it operates at lower speeds in commercial service. These feats demonstrate the continual push for faster and more efficient rail travel.
Environmental Impact of Bullet Trains

Bullet trains offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to air and road travel. They produce significantly lower CO2 emissions per passenger compared to airplanes and cars. For example, a journey on a high-speed train can emit up to 90% less CO2 than a flight between the same destinations. This makes bullet trains a critical component in efforts to reduce carbon footprints globally.
In addition to lower emissions, bullet trains consume less energy per kilometer than other forms of transport. Their efficiency is due to the use of electricity, which can be sourced from renewable energy. As nations strive to meet climate targets, the expansion of high-speed rail networks offers a sustainable solution for reducing environmental impact while accommodating growing travel demands.
Technological Innovations in Bullet Trains

Technological advancement is at the heart of bullet train development. The use of magnetic levitation, as seen in the L0 Series Maglev, is a prime example of how technology is pushing the boundaries of speed and efficiency. Innovations in materials, aerodynamics, and propulsion systems continue to improve performance and passenger comfort.
Moreover, advances in signaling and communication systems have enhanced safety and operational efficiency. The European Train Control System (ETCS) and Japan’s Automatic Train Control (ATC) are crucial technologies that ensure trains run smoothly and safely at high speeds. As technology evolves, bullet trains will continue to incorporate the latest advancements to enhance their capabilities.
Global Expansion of Bullet Train Networks

Since the launch of the Shinkansen, bullet train networks have expanded across the globe. Europe boasts an extensive high-speed rail network, with France, Spain, and Germany leading the way. The TGV in France and the AVE in Spain are renowned for their speed and efficiency, connecting major cities across their respective countries.
China has rapidly developed the world’s largest high-speed rail network, with over 38,000 kilometers of track. The network connects major cities, reducing travel times and promoting economic development. Other countries, including the United States and India, are also exploring high-speed rail projects to enhance their transportation infrastructure.
Safety Features of Bullet Trains

Bullet trains are equipped with advanced safety features that make them one of the safest modes of transport. Automatic train protection systems, earthquake detection, and collision avoidance technologies ensure passenger safety. In Japan, the Shinkansen has maintained an impeccable safety record with no fatal accidents due to derailments or collisions since it began operation in 1964.
Regular maintenance and inspections further enhance safety. For example, tracks and trains are routinely checked for wear and tear, ensuring they meet stringent safety standards. Moreover, the use of dedicated tracks for high-speed services reduces the risk of accidents, offering passengers peace of mind when traveling.
Economic Impact of Bullet Trains

Bullet trains have a significant economic impact, fostering regional development and job creation. By reducing travel times, they facilitate business travel and tourism, boosting local economies. The connectivity provided by high-speed rail enables businesses to reach a larger customer base and access new markets.
Moreover, the construction and maintenance of bullet train networks create numerous jobs, from engineering and construction to operations and management. In countries like China and Japan, high-speed rail has been instrumental in driving economic growth and enhancing urban development.
Cultural Significance of Bullet Trains in Japan

In Japan, bullet trains are more than just a means of transportation; they are a cultural icon. The Shinkansen represents the country’s technological prowess and commitment to innovation. It has become a symbol of modern Japan, appearing in films, literature, and even as themed merchandise.
The punctuality and efficiency of the Shinkansen are highly regarded, reinforcing Japan’s reputation for precision and reliability. The experience of traveling on a Shinkansen is often described as quintessentially Japanese, offering a glimpse into the nation’s dedication to excellence and hospitality.
Future Developments in Bullet Train Technology

The future of bullet trains promises even greater advancements in speed, efficiency, and sustainability. Research is underway to improve maglev technology, with countries like Japan and China leading the charge. Developments in energy efficiency, such as regenerative braking and lightweight materials, are also on the horizon.
Additionally, innovations in passenger experience are expected. Concepts like onboard Wi-Fi, personalized services, and enhanced seating comfort are becoming standard. As high-speed rail continues to evolve, it will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of transportation, offering faster, greener, and more convenient travel options.
Unique Design Features of Bullet Trains

Bullet trains are renowned for their sleek and aerodynamic designs, which are not only visually striking but also serve to minimize air resistance and maximize speed. The iconic nose shape of Japan’s E5 Series Shinkansen, for instance, is inspired by the kingfisher bird’s beak, allowing it to cut smoothly through the air.
Interior design is also a focus, with attention to passenger comfort and convenience. Spacious seating, large windows, and quiet cabins create a pleasant travel experience. The design of bullet trains reflects a careful balance between form and function, ensuring they remain at the forefront of modern transportation.
Like Fast Lane Only’s content? Be sure to follow us.
Here’s more from us:
*Created with AI assistance and editor review.






Leave a Reply