The automobile dashboard has undergone significant transformation since the early days of motoring. From simple wooden panels to today’s digital interfaces, dashboard layouts have evolved to enhance driver experience and vehicle control. This journey through dashboard design and technology reveals how the focus has shifted from basic functionality to advanced connectivity and personalization, reflecting broader changes in automotive technology and consumer expectations.
Early Days of Automobile Dashboards
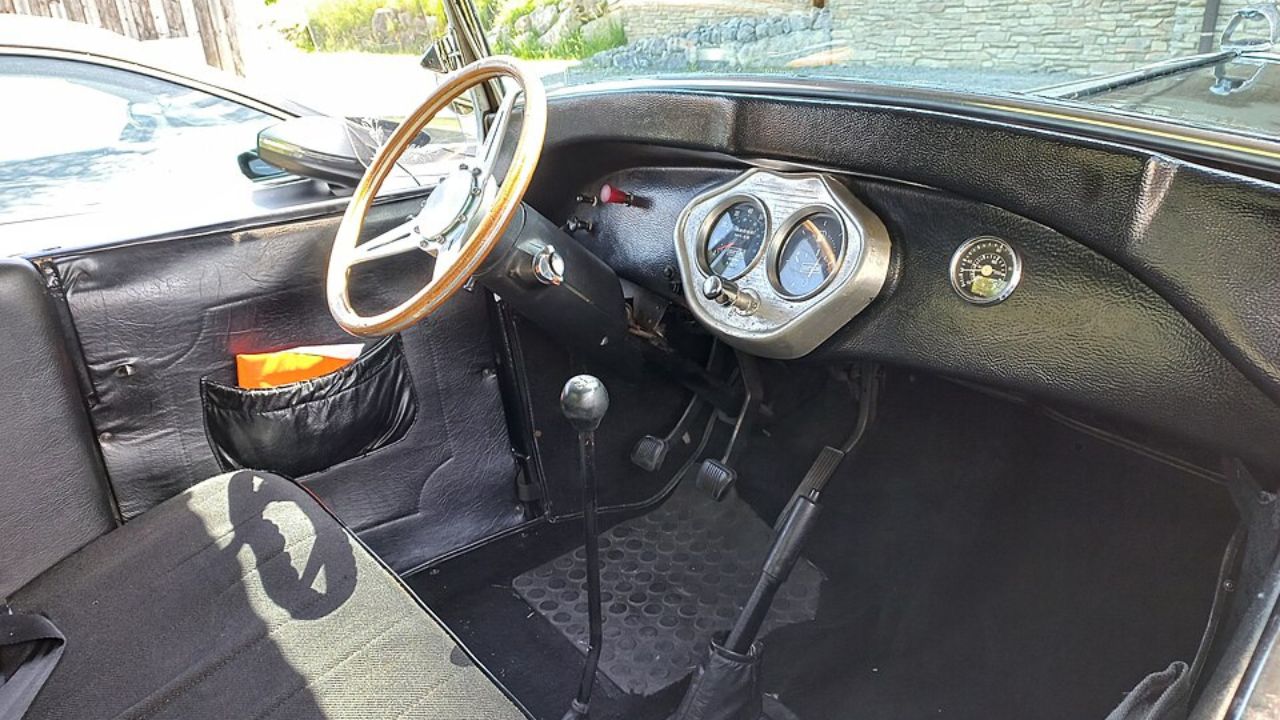

In the early 20th century, the automobile dashboard was a far cry from today’s sophisticated systems. These rudimentary dashboards were often made of wood, serving as simple panels that offered essential information to the driver. The primary purpose was to protect the driver from the mechanical components of the vehicle, rather than to provide detailed information or control functions. Early dashboards typically featured only the most basic instruments, such as an ammeter or a simple oil pressure gauge, if any at all.
As automobiles became more complex and widespread, there was a growing need for more detailed information to be available to the driver. The 1920s and 1930s saw the introduction of essential gauges such as the speedometer and fuel gauge, which became standard features in many vehicles. These instruments provided drivers with critical data necessary for safe and efficient driving. For example, the 1930 Ford Model A introduced a dashboard with a speedometer in the center, flanked by an ammeter and fuel gauge, marking a significant step towards more informative dashboard layouts.
Post-War Innovations and the Rise of Consumerism
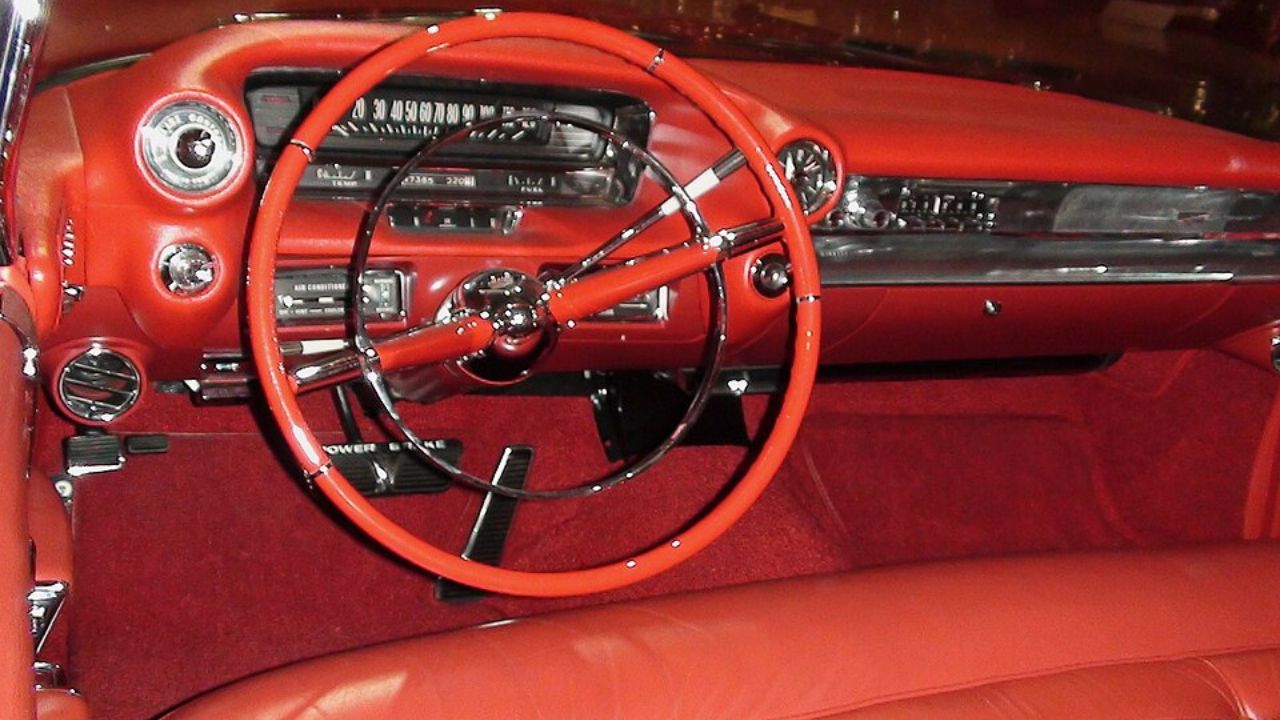

The post-war era of the 1950s and 1960s brought about significant changes in dashboard design, driven by a wave of consumer prosperity and a booming automotive industry. This period marked a shift towards more stylish and visually appealing dashboards, with automakers focusing on aesthetics as well as functionality. The dashboards of this era featured vibrant colors, chrome accents, and sweeping designs that mirrored the flamboyant exterior styling of the cars themselves. A prime example is the 1959 Cadillac Eldorado, which boasted a dashboard that was as glamorous as the car’s exterior.
Alongside these stylistic changes, there was an increased focus on comfort and convenience, reflecting the growing consumer demand for more luxurious and feature-rich vehicles. Radios became a staple in car dashboards, offering entertainment options for drivers and passengers alike. Air conditioning controls, initially a luxury feature, started to become more common, allowing drivers to control the cabin environment with ease. By the 1960s, the dashboard had evolved into a command center of sorts, integrating features that enhanced both the driving experience and passenger comfort.
The Digital Revolution of the 1980s and 1990s
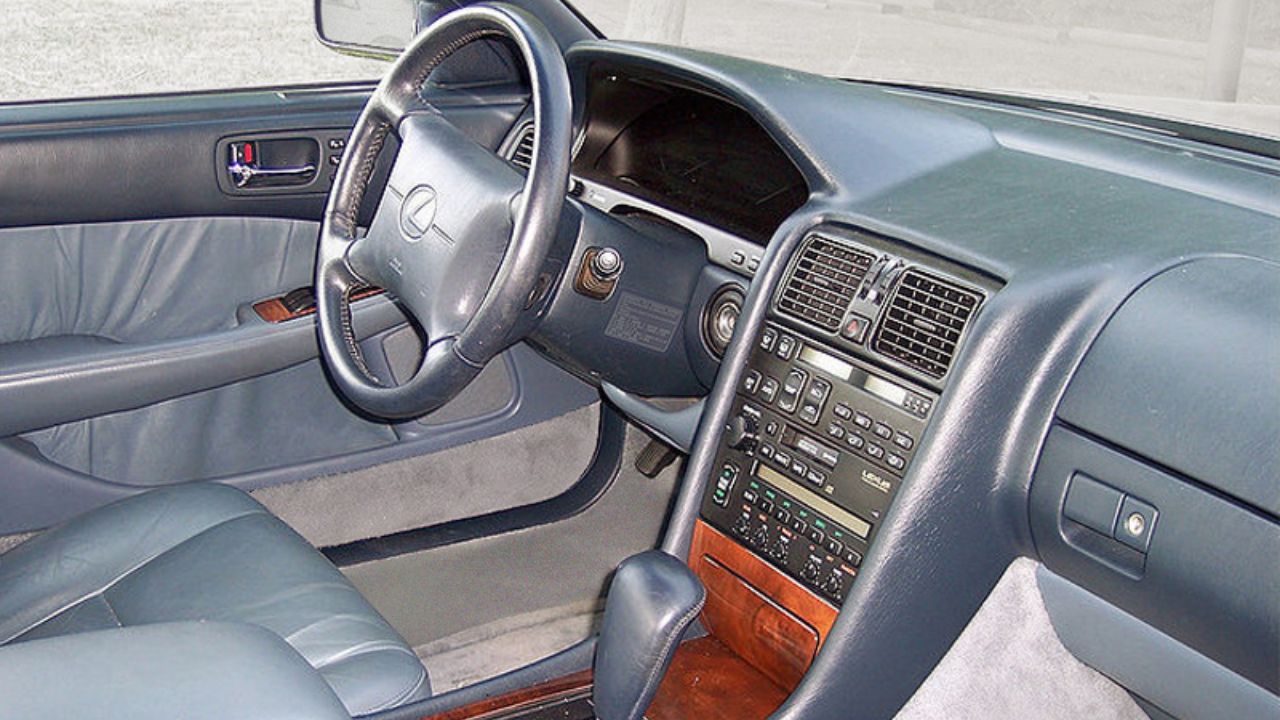

The 1980s and 1990s represented a digital revolution in automobile dashboard design, as manufacturers began to incorporate electronic technologies into their vehicles. This era saw the introduction of digital displays, which gradually replaced traditional analog dials and gauges. These digital dashboards offered a more futuristic look and provided drivers with new ways to interact with their vehicles. For instance, the 1986 Nissan 300ZX Turbo featured a digital dashboard that displayed speed, fuel level, and other vital information in a sleek, high-tech format.
During this time, electronic systems such as cruise control and early navigation systems began to find their way into dashboards. The integration of these technologies marked a significant shift in how vehicles were designed and operated. The 1990 Lexus LS400, for example, offered a sophisticated dashboard layout with electronic climate control and an early version of a navigation system, showcasing the potential of digital technology to enhance driver convenience and vehicle functionality.
21st Century: The Era of Connectivity and Customization
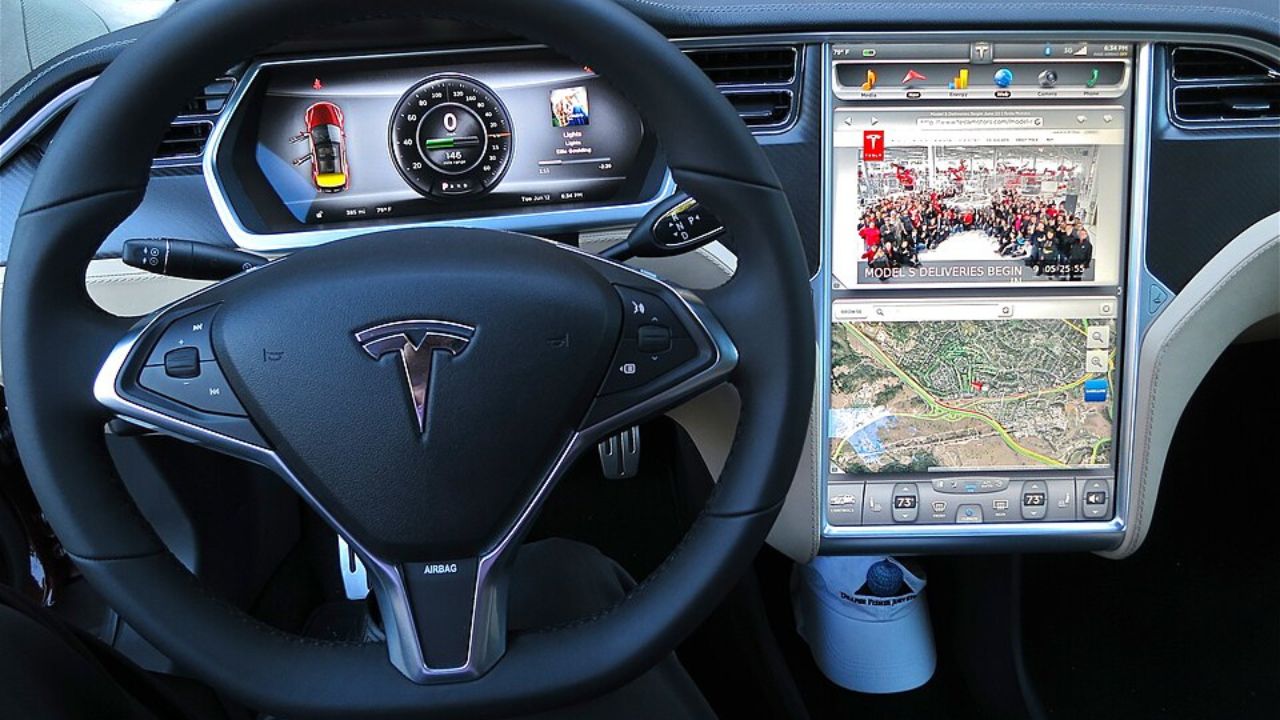
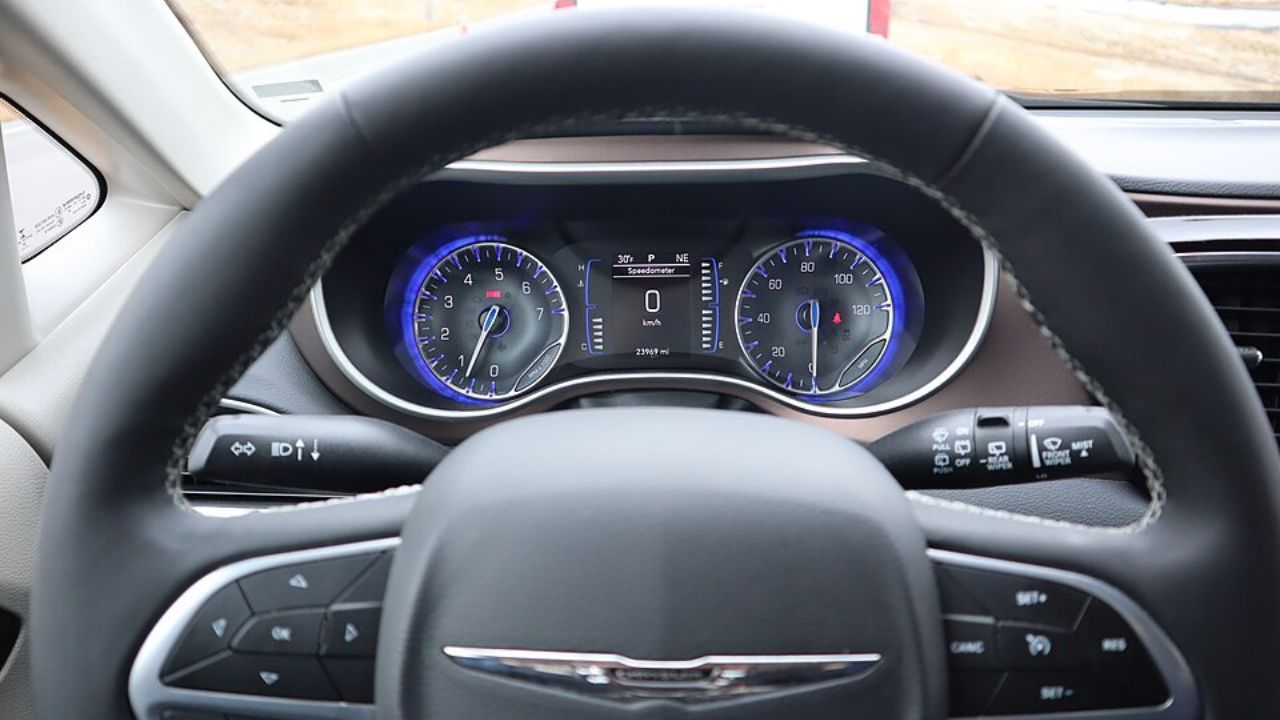
As we entered the 21st century, the advent of the internet and advances in digital technology brought about a new era in dashboard design. Touchscreens and advanced infotainment systems became the norm in modern vehicles, offering a range of features that were unthinkable in earlier decades. These systems allowed drivers to access navigation, music, and communication tools with ease, all from a central interface. The Tesla Model S, introduced in 2012, became famous for its large touchscreen display that controlled almost all vehicle functions, setting a new standard for dashboard technology.
Today’s dashboards also emphasize customization and personalization, allowing drivers to tailor their interfaces to suit their preferences. Digital instrument clusters can be configured to display a wide range of information, from traditional speed and fuel data to more advanced options like real-time traffic updates and vehicle diagnostics. Personalization options extend to infotainment systems as well, with drivers able to choose themes, set up profiles, and integrate with smartphones for a seamless driving experience. This level of customization reflects a broader trend towards making vehicles more adaptable to individual needs and lifestyles.
Future Trends in Dashboard Design
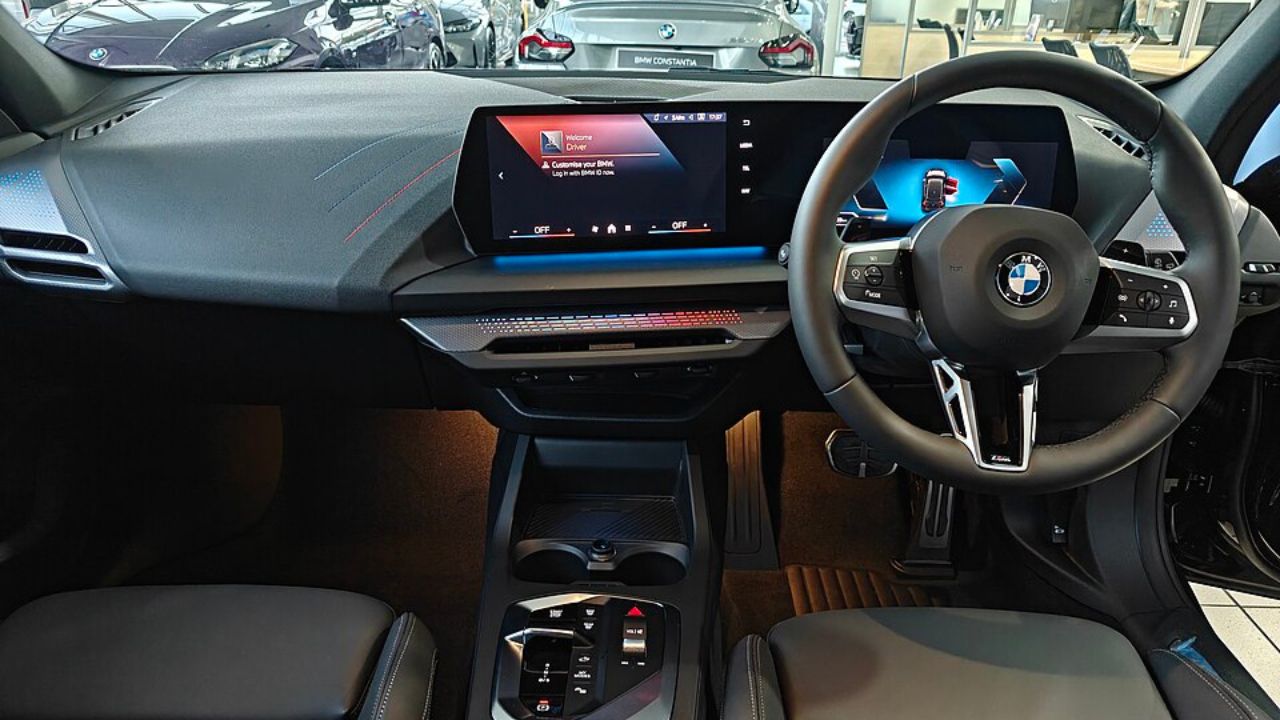

Looking ahead, the future of dashboard design is set to be shaped by emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI). AR displays have the potential to overlay navigational cues and important information directly onto the windshield, providing drivers with a more intuitive and immersive experience. AI-driven interfaces could offer predictive suggestions and intelligent assistance, learning from driver habits to offer a more personalized and proactive experience. Automakers like BMW and Mercedes-Benz are already experimenting with these technologies, hinting at a future where dashboards are more interactive and intelligent than ever before.
Sustainability and minimalist design are also expected to play a significant role in the evolution of dashboards. As environmental concerns continue to influence consumer preferences, automakers may opt for eco-friendly materials and more streamlined designs that reduce complexity and enhance efficiency. This shift could see dashboards become simpler and more focused, with an emphasis on functionality over form. The move towards electric vehicles is likely to accelerate these trends, as manufacturers seek to create interiors that reflect the clean and sustainable ethos of their powertrains.
Like Fast Lane Only’s content? Be sure to follow us.
Here’s more from us:
*Created with AI assistance and editor review.







Leave a Reply