Waymo’s self-driving cars have been turning heads for years, evolving from Google’s early experiments into a real-world service. With their sleek Jaguar I-PACE SUVs zipping through cities like San Francisco and Phoenix, they’re redefining how we think about getting around. This article lays out 10 key facts about Waymo’s autonomous vehicles, covering their tech, city use, and broader impact. Whether you’re a car buff or just curious about the future of transportation, these insights will give you a clear picture of what Waymo’s up to.
1. Roots in Google’s Big Bet
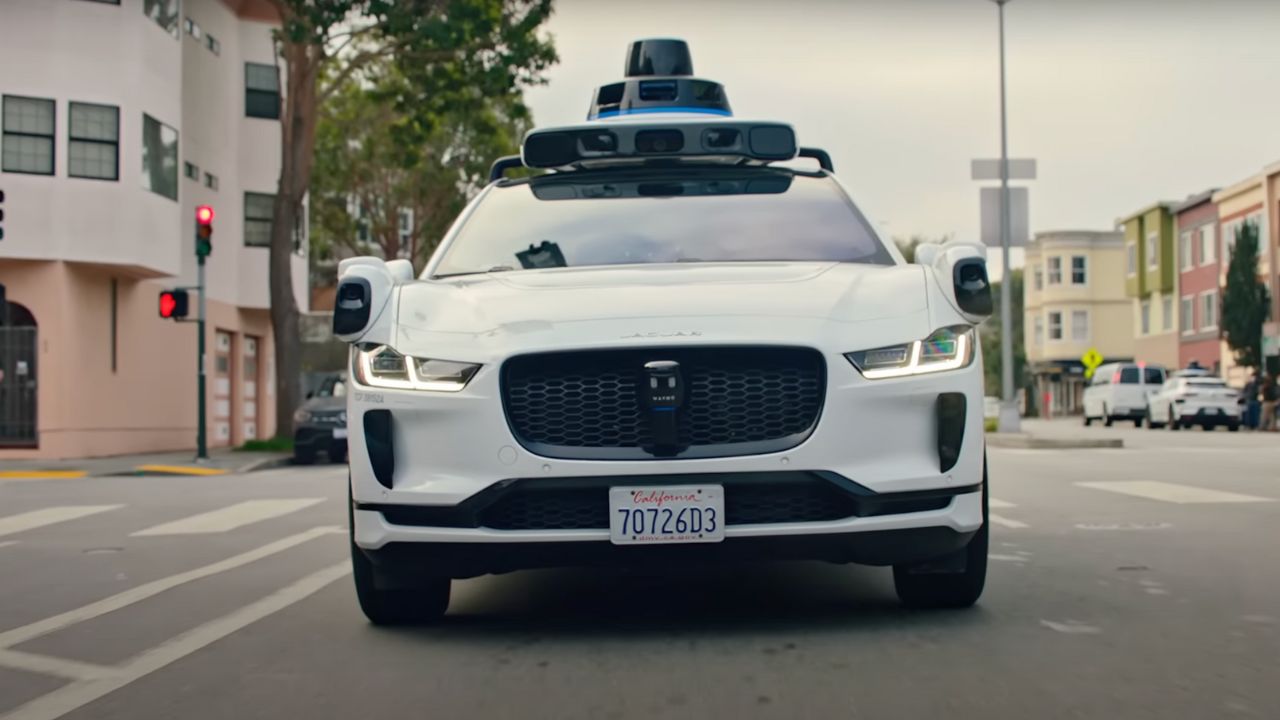

Waymo started as Google’s self-driving car project in 2009, born in the X lab alongside wild ideas like Project Loon. Engineers like Sebastian Thrun pushed to make fully autonomous driving a reality, not just driver-assist tech. By 2016, it spun off into Waymo under Alphabet, focusing on ride-hailing. Over $1.1 billion went into development by 2015, showing Google’s serious commitment. Today, Waymo’s tech is a leader in the field, with millions of miles driven, proving it’s not just a side project but a game-changer.
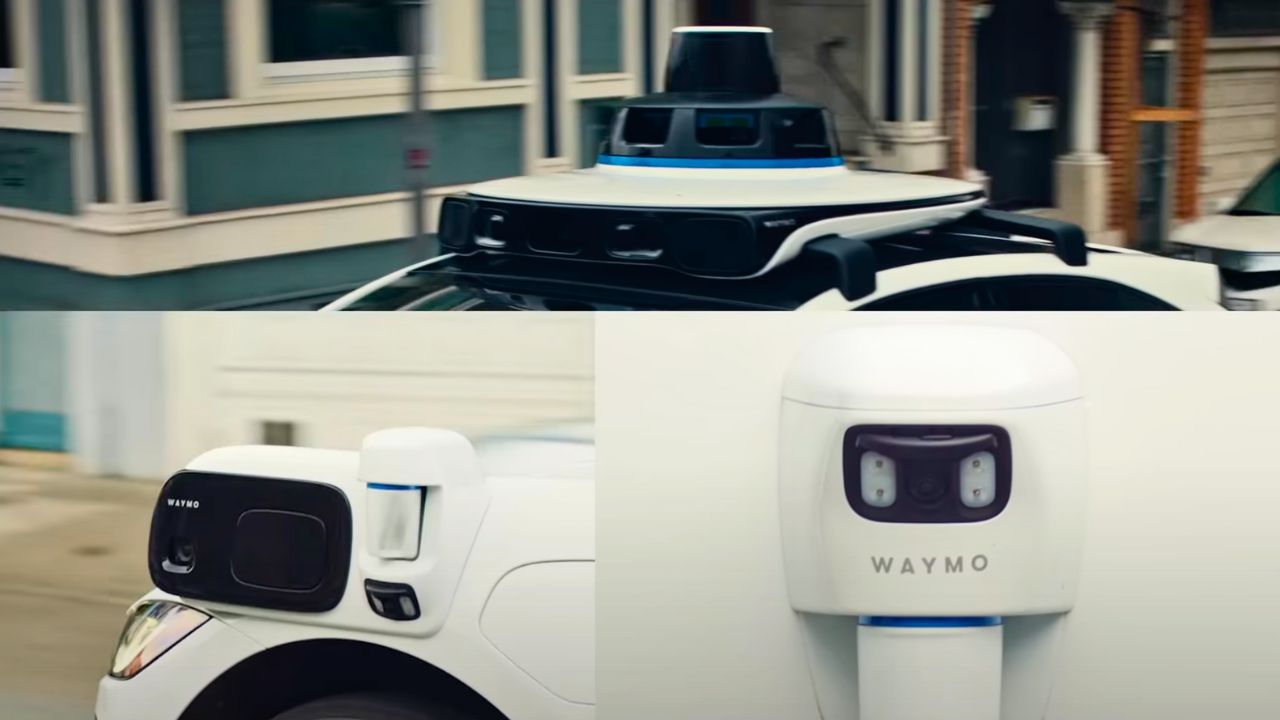
2. Sensor Suite That Sees Everything
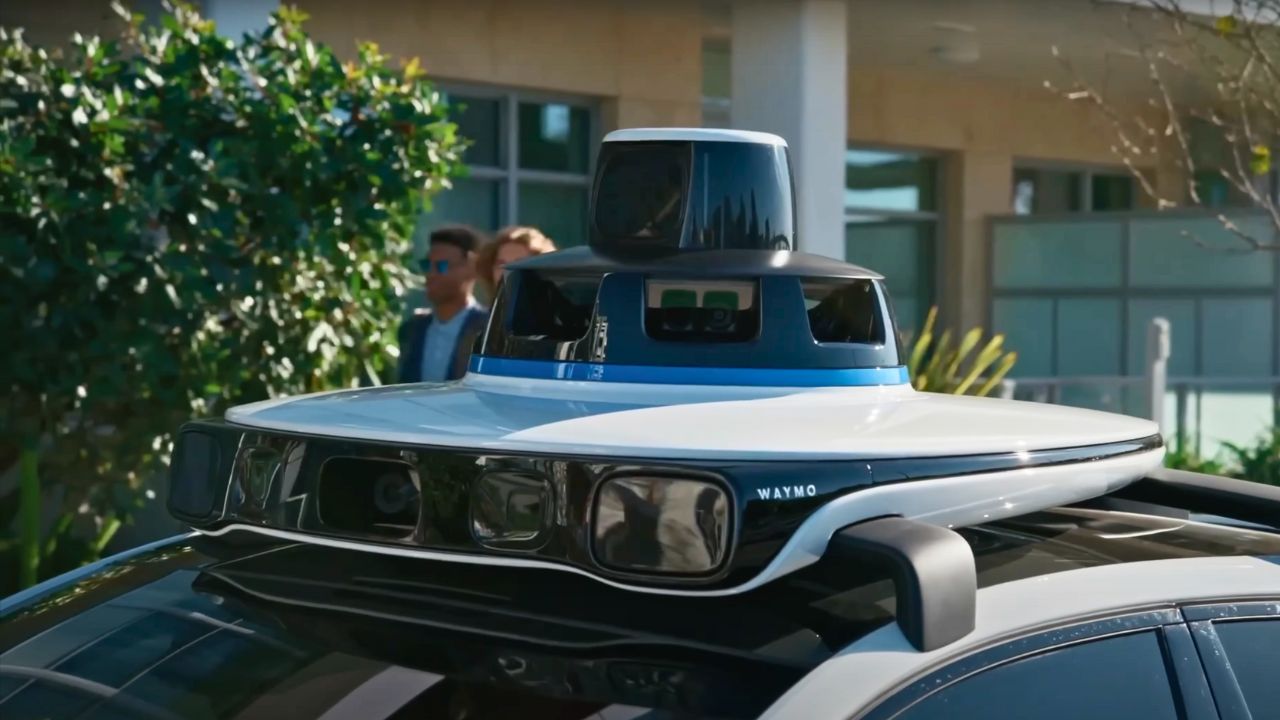

Waymo’s cars use a mix of lidar, radar, and 29 cameras to create a 360-degree view, spotting pedestrians or traffic lights up to 500 meters away. Lidar builds a 3D map of the surroundings, while radar handles tough weather like rain or fog. The onboard computer crunches this data in real time, using AI to decide the safest moves. This setup lets the car navigate complex city streets without a human driver, making it reliable even in chaotic urban settings.
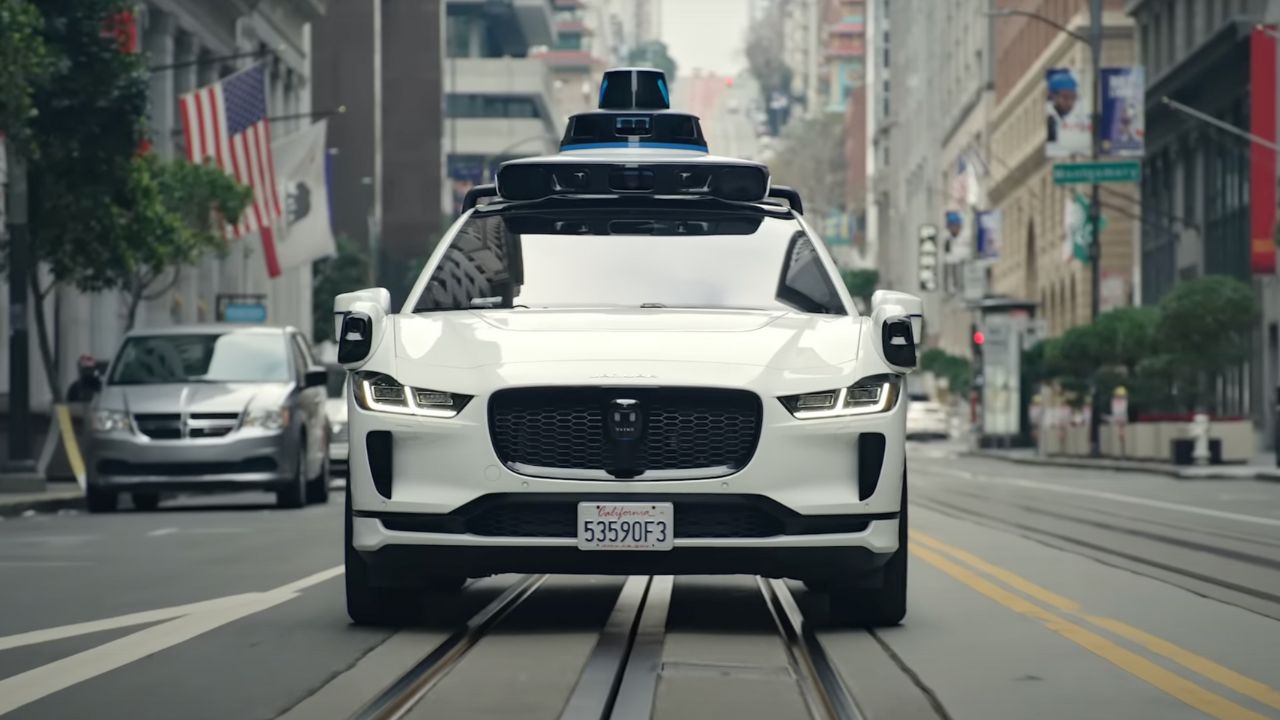
3. Fully Autonomous, No Steering Wheel
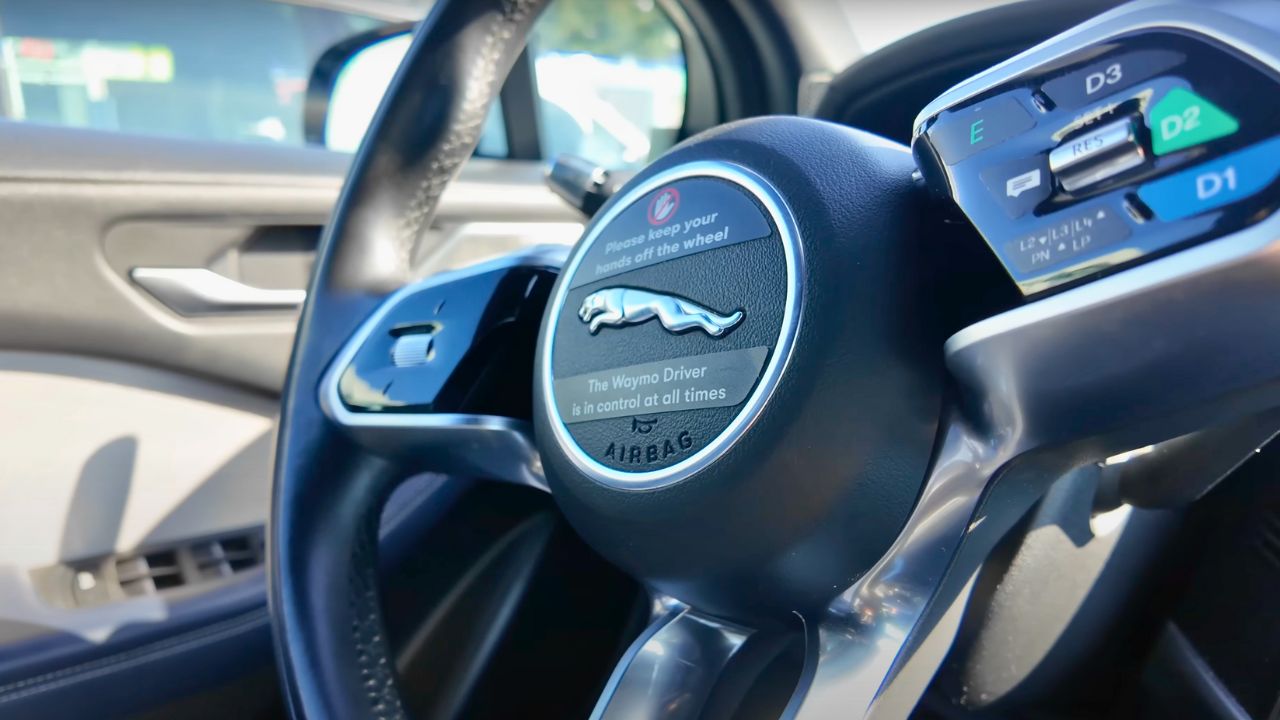

Unlike Tesla’s Autopilot, Waymo’s vehicles are Level 4 autonomous, meaning they drive without human input in specific areas. The Jaguar I-PACE models have no steering wheel or pedals, just seats for passengers. In 2015, Waymo gave the first fully driverless ride on public roads to a legally blind passenger in Austin. This hands-off approach defines Waymo’s mission: safe, accessible transport for everyone, not just tech for human drivers to lean on. It’s a big leap toward a driverless future.
4. City Ride-Hailing in Action
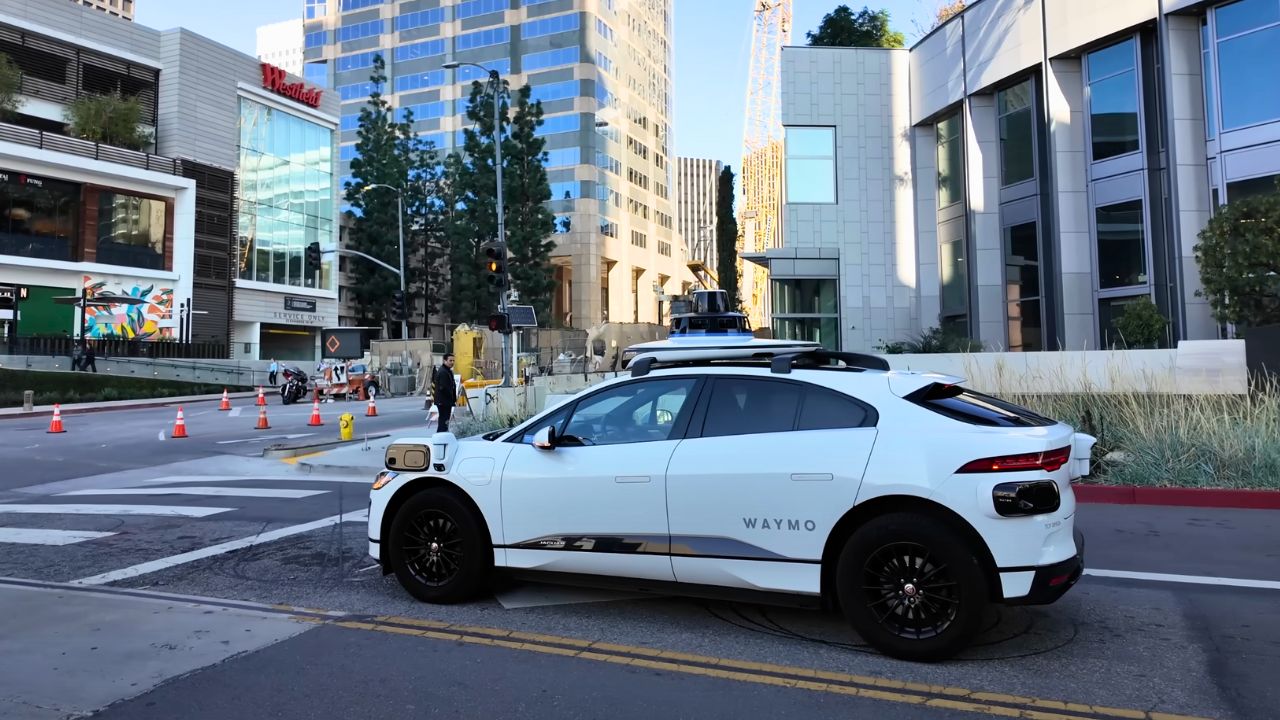

Waymo One, their ride-hailing service, operates in Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and more, covering 315 square miles in some areas. You book a ride via the Waymo app, and an electric I-PACE picks you up, no driver needed. As of April 2025, they’re doing 250,000 paid rides weekly, clocking over 1 million miles. Partnerships with Uber in Austin and Atlanta expand their reach. It’s like a taxi service, but with AI behind the wheel, easing city congestion.
5. Safety Stats That Stand Out

Waymo’s safety record is strong, with 7.1 million rider-only miles showing fewer crashes than human drivers. Their data suggests 17 fewer injuries and 20 fewer police-reported crashes compared to human benchmarks in cities like Phoenix and San Francisco. The cars’ sensors and AI react faster than humans, avoiding hazards like red-light runners. While no system’s perfect, Waymo’s transparency with crash data builds trust, showing they’re serious about keeping roads safer for everyone.
6. AI That Thinks Like a Driver
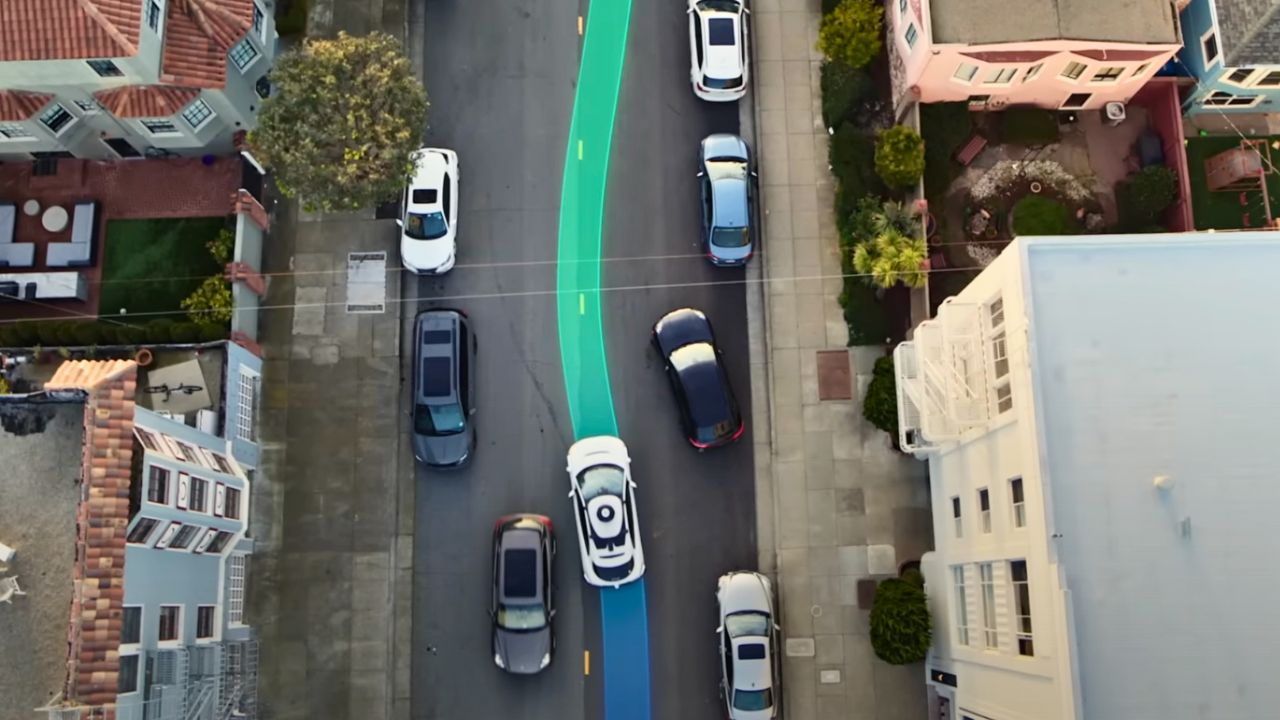

The Waymo Driver, their AI system, answers four key questions: Where am I? What’s around me? What’ll happen next? What should I do? It uses detailed maps, sensor data, and machine learning to predict other road users’ moves, like a cyclist swerving. This lets it plan smooth routes, adjust speed, or stop for emergency vehicles. Constant updates from real-world driving data make it smarter, helping it handle tricky urban scenarios with human-like judgment.
7. Electric Fleet for a Greener Ride
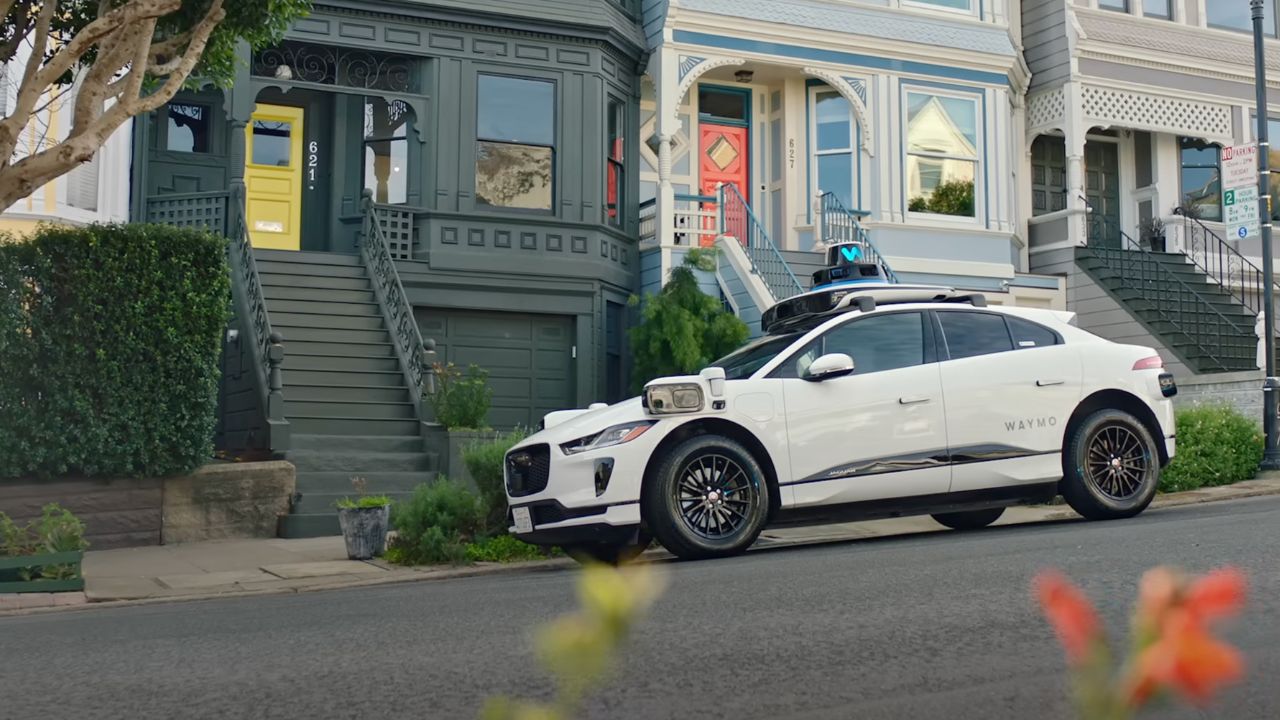

Waymo’s entire fleet is electric, using Jaguar I-PACE SUVs and soon Zeekr vehicles, cutting down on emissions. Their charging partners keep the cars ready 24/7, supporting city sustainability goals. In places like Los Angeles, where air quality’s a concern, this matters. Passengers get a quiet, eco-friendly ride, and Waymo’s focus on electric vehicles aligns with broader pushes for cleaner urban transport. It’s a practical step toward greener cities without sacrificing convenience.
8. Cultural Shift in Mobility
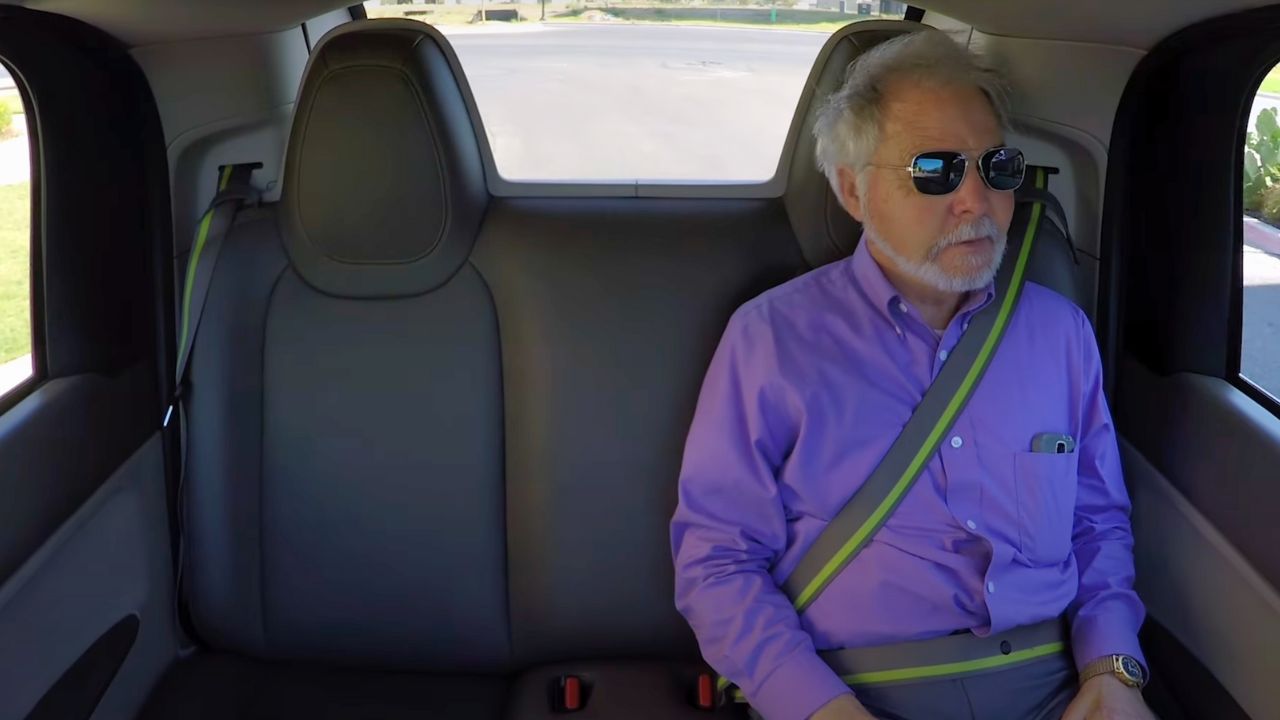

Waymo’s cars are changing how we view transportation. They offer freedom for non-drivers, like the elderly or visually impaired, who can now travel independently. In cities, they could reduce the need for personal car ownership, freeing up parking space and easing traffic. But there’s pushback—some worry about job losses for drivers or tech glitches. Waymo’s gradual rollout aims to build public trust, showing autonomy can coexist with human needs. It’s reshaping urban life, one ride at a time.
9. Testing Grounds Like Carcraft
Waymo’s Carcraft simulation platform runs 25,000 virtual cars through digital cities, logging 8 million miles daily. It recreates real-world scenarios, like Austin’s roundabouts, to train the AI without risking actual roads. This virtual testing catches edge cases—like erratic drivers—before they happen in real life. Combined with physical test sites in California, it ensures the Waymo Driver is ready for anything. This behind-the-scenes work is why their cars handle complex urban environments so well.
10. Expanding Global Reach
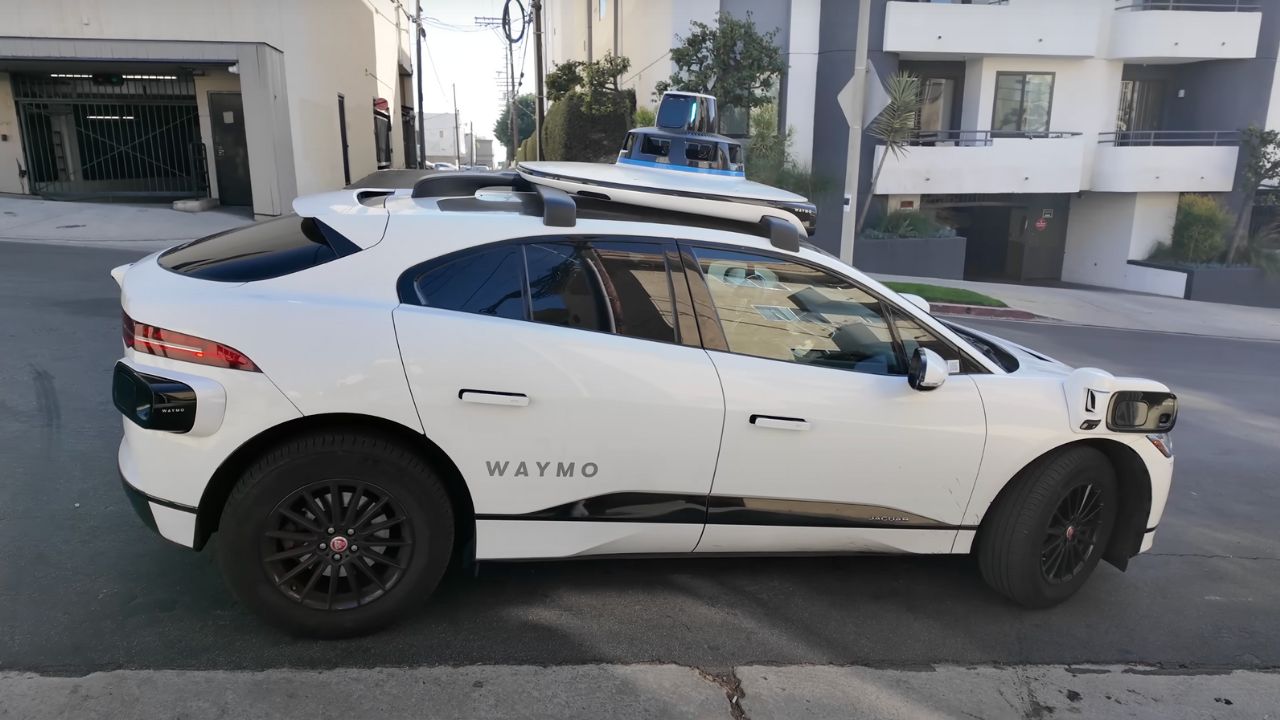

Waymo’s not stopping at the U.S. They’re planning services in Tokyo and Atlanta, partnering with local firms like Nihon Kotsu to map international roads. In 2024, they raised $5.6 billion to fuel this growth. Each new city requires custom mapping and testing to adapt to local driving habits. This global push could make Waymo a standard for urban transport worldwide, but it’ll take time to navigate diverse regulations and cultures. The future’s wide open.
Like what you read? Here’s more by us:







Leave a Reply